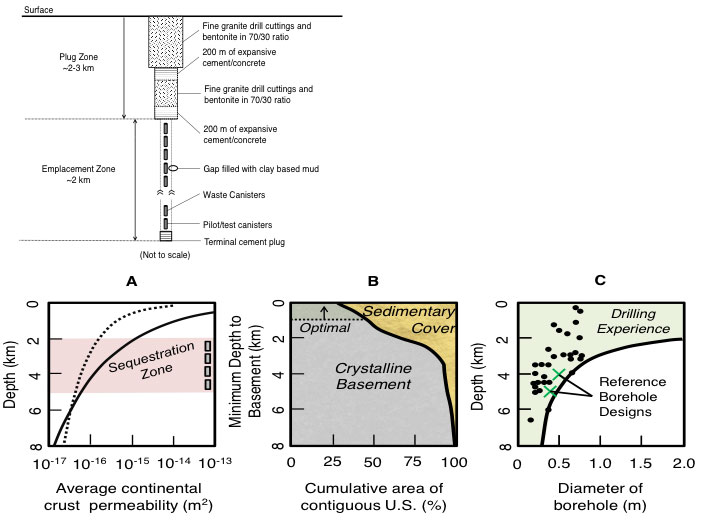
Deep borehole disposal of spent nuclear fuel offers the prospect of permanently sequestering high-level radioactive waste in 4-5 km deep boreholes drilled into low-permeability granitic bedrock, well below surface faults and aquifers, thus greatly reducing the number of radionuclide pathways into the biosphere. MIT research centers on simulation of radionuclide transport within the rock, design of the borehole plug, and development of safe and cost-effective drilling, loading and operation strategies.